Open Labs in Tunisia's textile sector
Participatory Innovation & Learning
How can the open lab concept be sustainably transferred to improve the research and innovation landscape?
This question forms the basis of the collaborative pilot project Places of Incubovation (PISWI), which aims to close technological learning, production, and innovation gaps by implementing OpenLabs to test feasibility and develop recommendations for action for the Tunisian textile sector.
Project Overview
The PISWI project focuses on the development, implementation, and dissemination of open labs as spaces for experiential technological learning, innovation, and open hardware development in Tunisia. Through the use of open source appropriate technology (OSAT), the aim is to create an infrastructure for open production and participatory value creation.
The initiative investigates how open production spaces and user-driven innovation contribute to local economic empowerment and research capacity building. Through a participatory research approach, users are involved from the outset to ensure that the results are relevant, scalable, and embedded in local socioeconomic contexts.
In addition, the project develops business models, teaching modules, and policy recommendations to promote sustainable innovation ecosystems.
Key Points
- Establishment and testing of Open Labs for local production and learning
- Development and implementation of teaching modules on open source hardware, business model development, and idea generation, as well as sustainable operating models for open labs, to empower participants to engage in independent, sustainable, and innovative economic activity.
- Application of OSAT in digital manufacturing, hardware prototyping, and product design
- Academic and professional training in open hardware and entrepreneurial skills
- Participatory research and exploratory case studies
- Strong links between science, industry, and innovation policy
- Contribution to German-Tunisian research and development cooperation
OpenLab Neotex 4.0
The first OpenLab in Monastir, Tunisia.
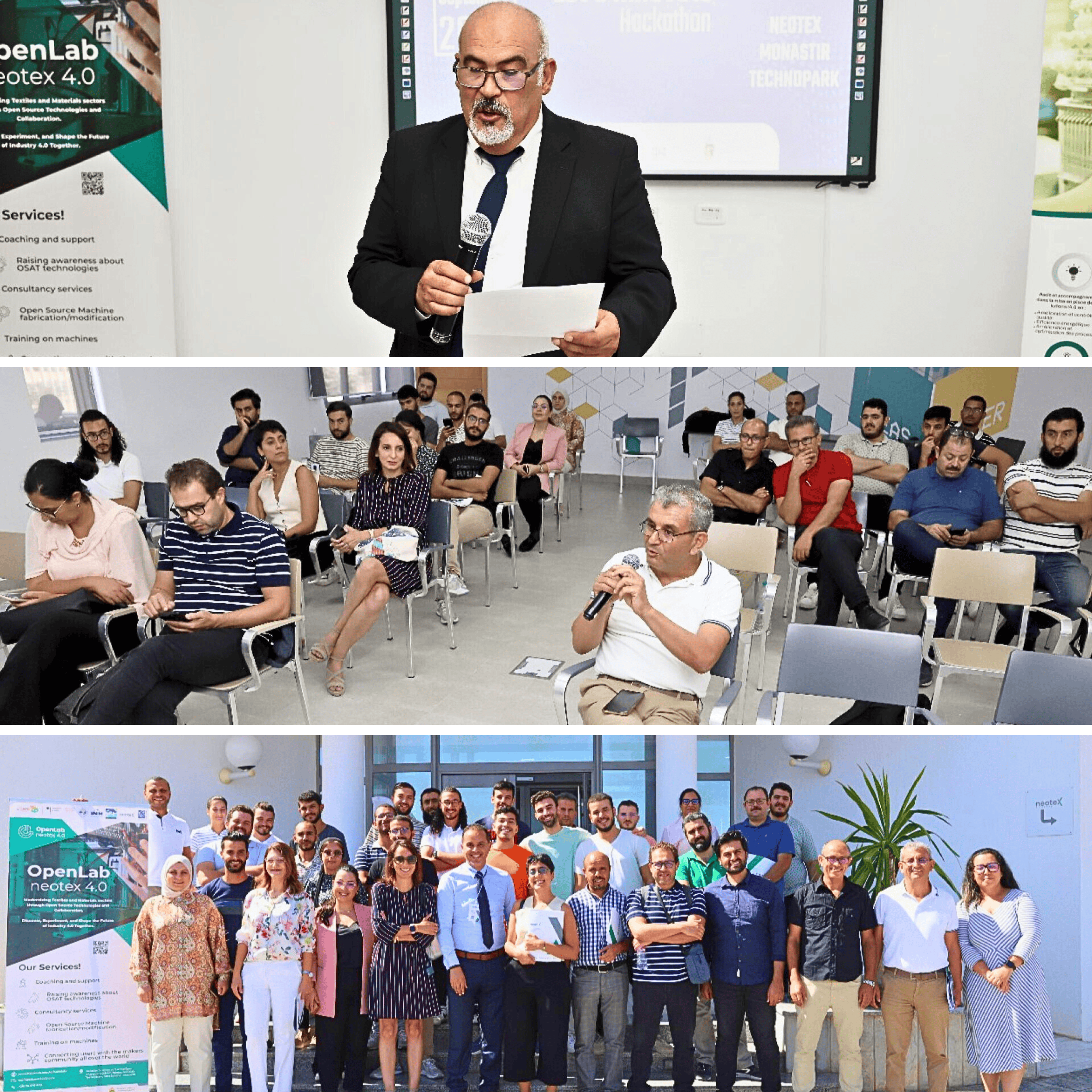
The OpenLab Neotex 4.0 is part of the PISWI project, which promotes the development of prototyping machines through digital manufacturing and the use of open-source technologies (hardware and software). In close cooperation between the Neotex 4.0 Center and the PISWI project, an innovative laboratory is being created here for the development and production of a networked, open textile machine (from: Collaborative innovation with Neotex Open Lab – Neotex 4.0 Center).
Blog-Article: OpenLab Neotex 4.0: Innovation und Zusammenarbeit vorantreiben | The New Production Institute
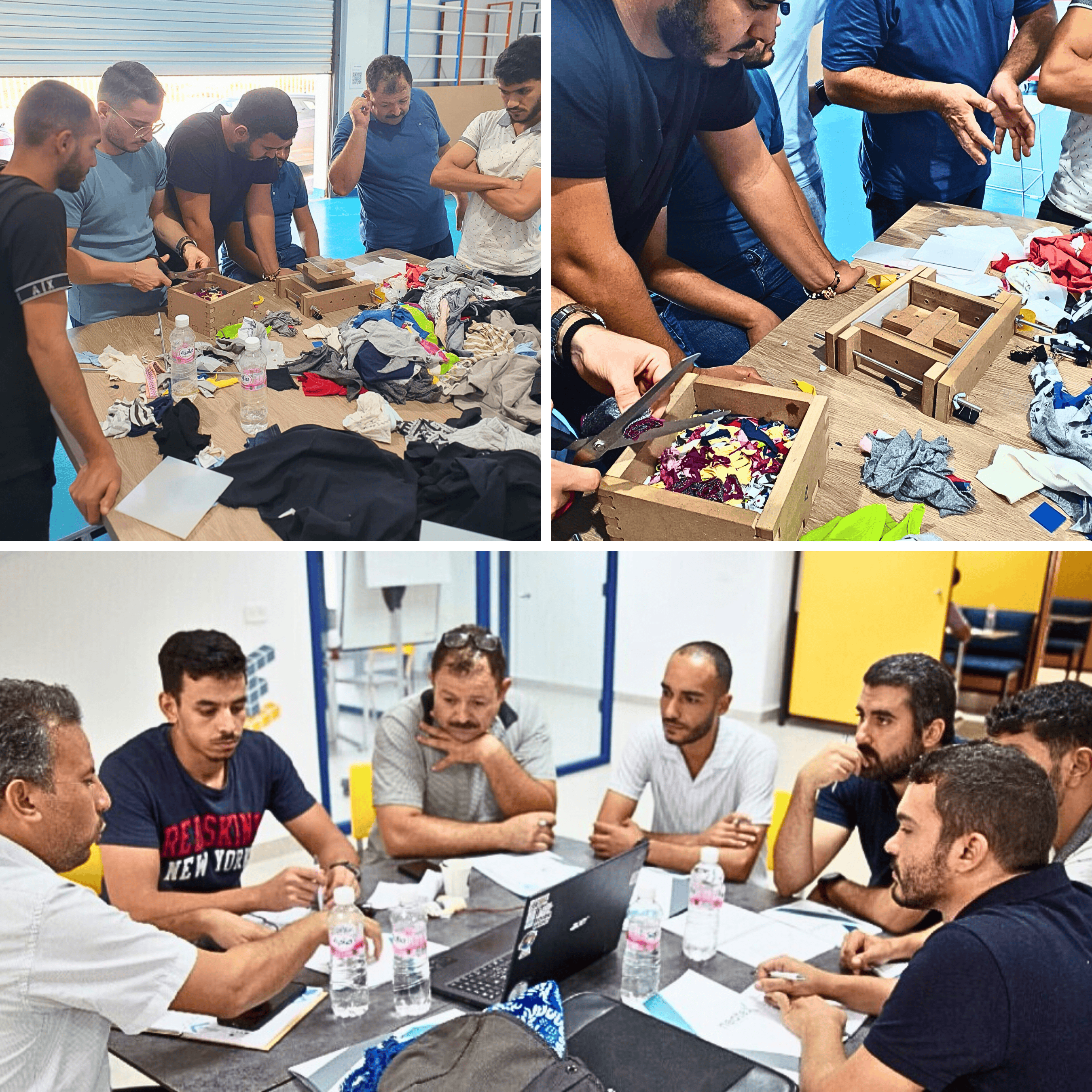
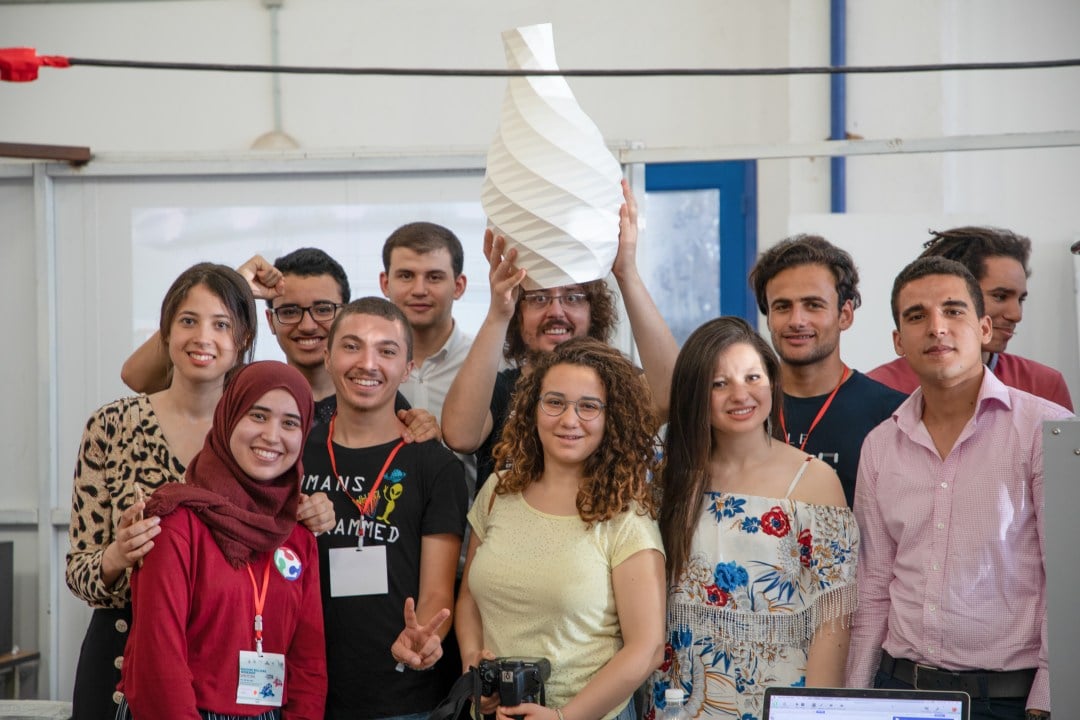

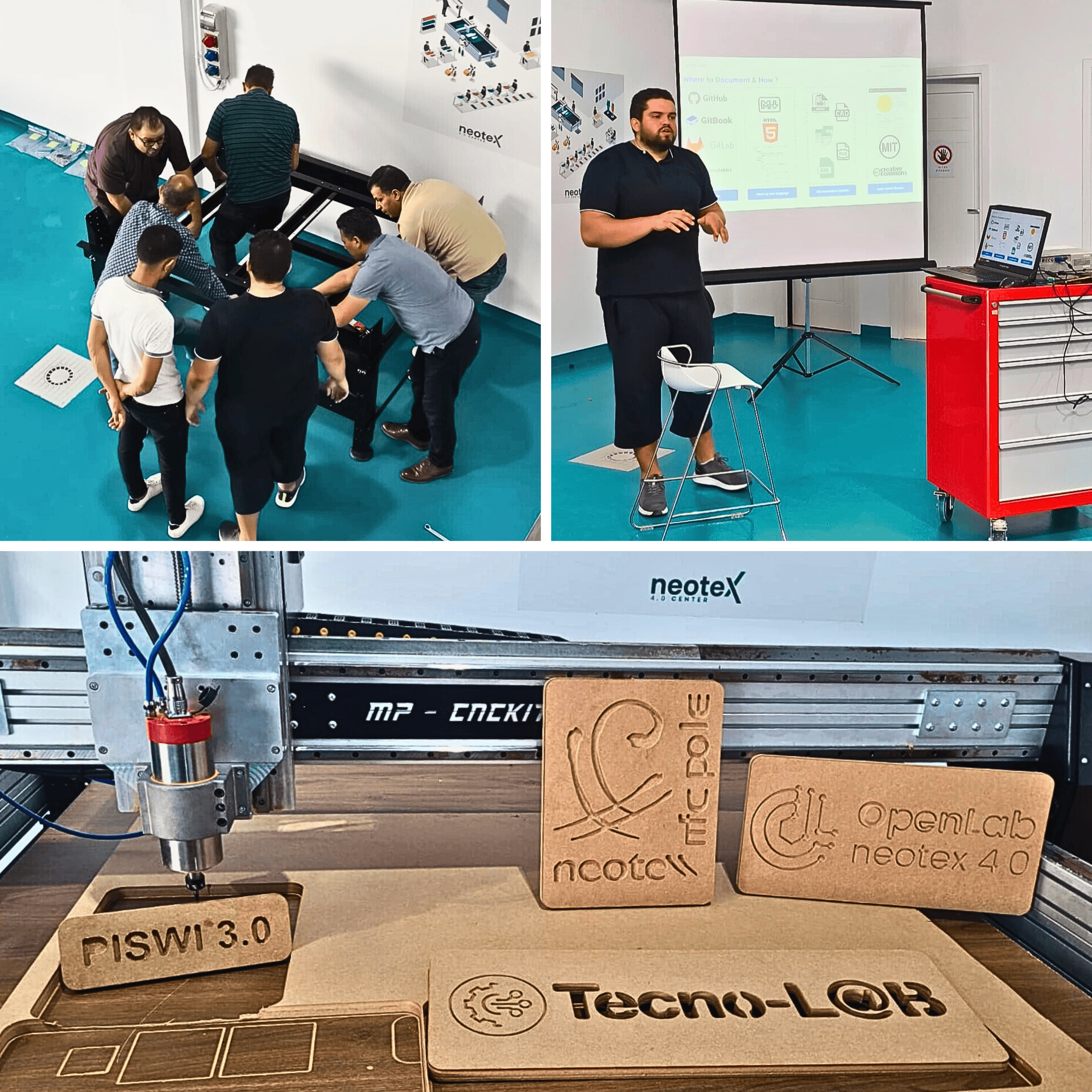


Key results
- Implementation of Open Labs tailored to the Tunisian textile sector – in particular through the opening of the OpenLab Neotex 4.0 in the city of Monastir (Tunisia). More in the blog article:: OpenLab Neotex 4.0: Innovation und Zusammenarbeit vorantreiben | The New Production Institute
- Mechanical engineering workshops with training courses for up to 80 participants and 20 instructors in the field of open-source machines
- Development of teaching modules for academic and dual training programs
- Exploratory case study on the validation of participatory innovation methods
- White paper with policy recommendations for strengthening Tunisia’s innovation landscape
- Strengthened bilateral research cooperation between Tunisia and Germany
Publications
Oladele-Emmanuel (2020)
Measuring and Managing User Innovation in Emerging Economies: Case Study of South West Nigeria, Dissertation, Helmut Schmidt University
Buxbaum-Conradi et al. (2019):
OPEN LABs: Erfahrungsbasiertes, vernetztes Lernen in offenen Produktionswerkstätten. Themenheft Lernen unter dem Aspekt der Vernetzung, Lernen&Lehren 135 (4/2019).
Partner
The project was carried out and the Open Lab implemented with local stakeholders from research and industry in the Tunisian textile sector. The research network is coordinated by staff at the New Production Institute and, in addition to Helmut Schmidt University, consists of the National Engineering School of Tunis (ENIT) – Tunis el Manar, the National Engineering School of Monastir (ENIM), the Institut Supérieur des Études Technologieques de Ksar Hellal (ISET), and the Monastir-El Fejja (la Manouba) competitiveness cluster (mfcpole).
Dictionary
Open Laboratories
Open Labs are shared, freely accessible production spaces that promote decentralized, user-driven innovation through digital manufacturing and OSAT. They support hands-on learning, local production, and community-based development.
OSAT
Open Source Appropriate Technology (OSAT) refers to technologies that are open source and at the same time adapted to local needs and resources. The aim is to develop technological solutions that are cost-effective, repairable, and locally reproducible—often with the help of digital manufacturing processes such as 3D printing or CNC milling.
Project title & duration
- Joint project: Pilot project to close technological learning, production, and innovation gaps by implementing OpenLabs to test feasibility and develop policy recommendations for the Tunisian textile sector
- 2021-2024






